Table of Contents
ToggleWorking Principle of Carbon Molecular Sieve to Produce Nitrogen
Carbon molecular sieve(CMS) is a key material for industrial nitrogen production, and its working principle mainly relies on selective adsorption separation technology. Below, we will detail the specific mechanism of how it achieves nitrogen purification, including its basic adsorption methods, the principle of separating nitrogen and oxygen from air, and the key factors affecting the separation effect.
Adsorption Separation Mechanism of Carbon Molecular Sieve
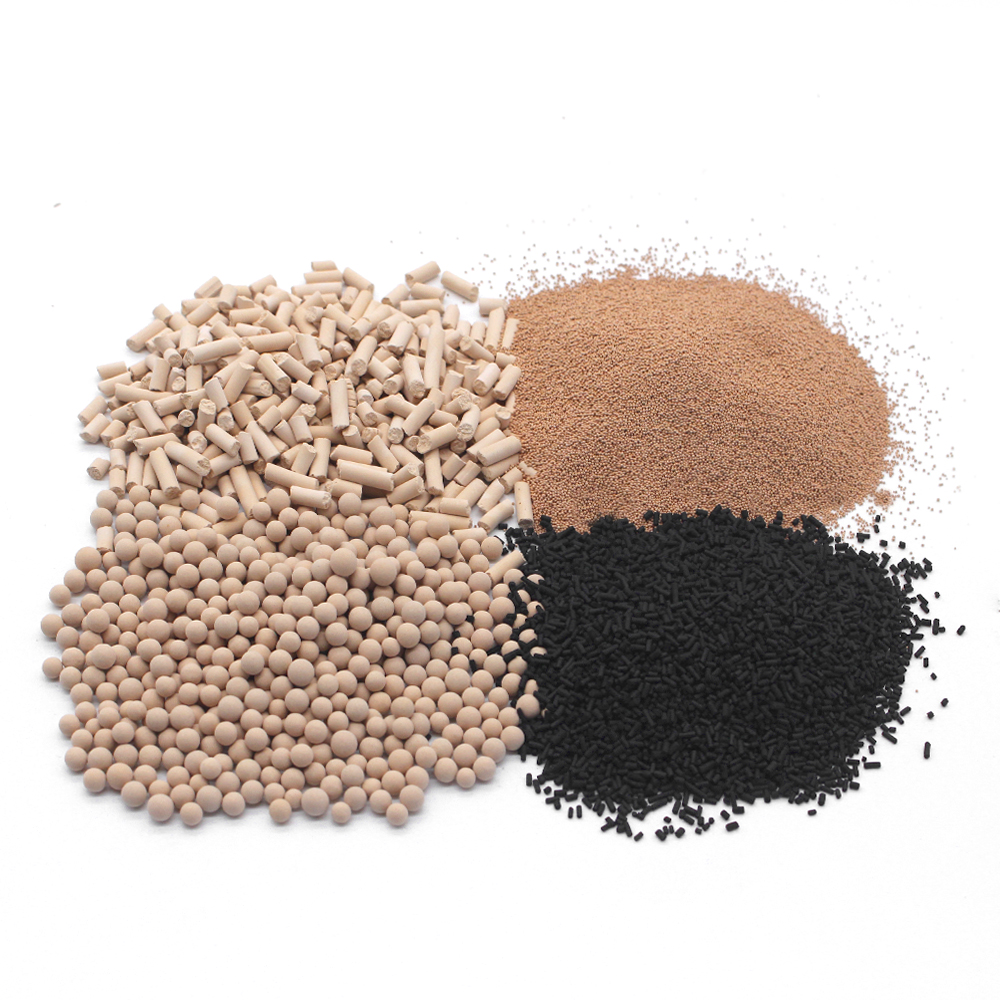
Carbon molecular sieves achieve adsorption separation by using the selective adsorption ability of porous solid materials to separate and purify gas or liquid mixtures. A complete adsorption separation process usually consists of cyclic operations of adsorption and desorption.

For nitrogen generation carbon molecular sieves, the adsorption separation process is mainly divided into two types: pressure swing adsorption (PSA) and temperature swing adsorption (TSA). Specifically, temperature swing adsorption completes the cyclic operation by adjusting the temperature; pressure swing adsorption, on the other hand, relies on physical adsorption processes driven by pressure changes. As a common adsorbent, carbon molecular sieves typically use the pressure swing adsorption method to separate nitrogen and oxygen in air, thereby achieving nitrogen purification.
Separation Principle of N₂ and O₂ in Air by Carbon Molecular Sieves
N2 and O2 in the separation of carbon molecular sieve in the air are based on the difference between the two in the diffusion rate. Both N2 and O2 are non -polar molecules, and the molecular diameter is very close (O2 is 0.28nm and N2 is 0.3nm. Because the physical properties of the two are similar, the binding force of the carbon molecular sieve zeolite is not much different. From the perspective of thermodynamics (absorbing balance) The adsorption of carbon molecular sieve on N2 and O2 is not selective, and it is difficult to separate the two.
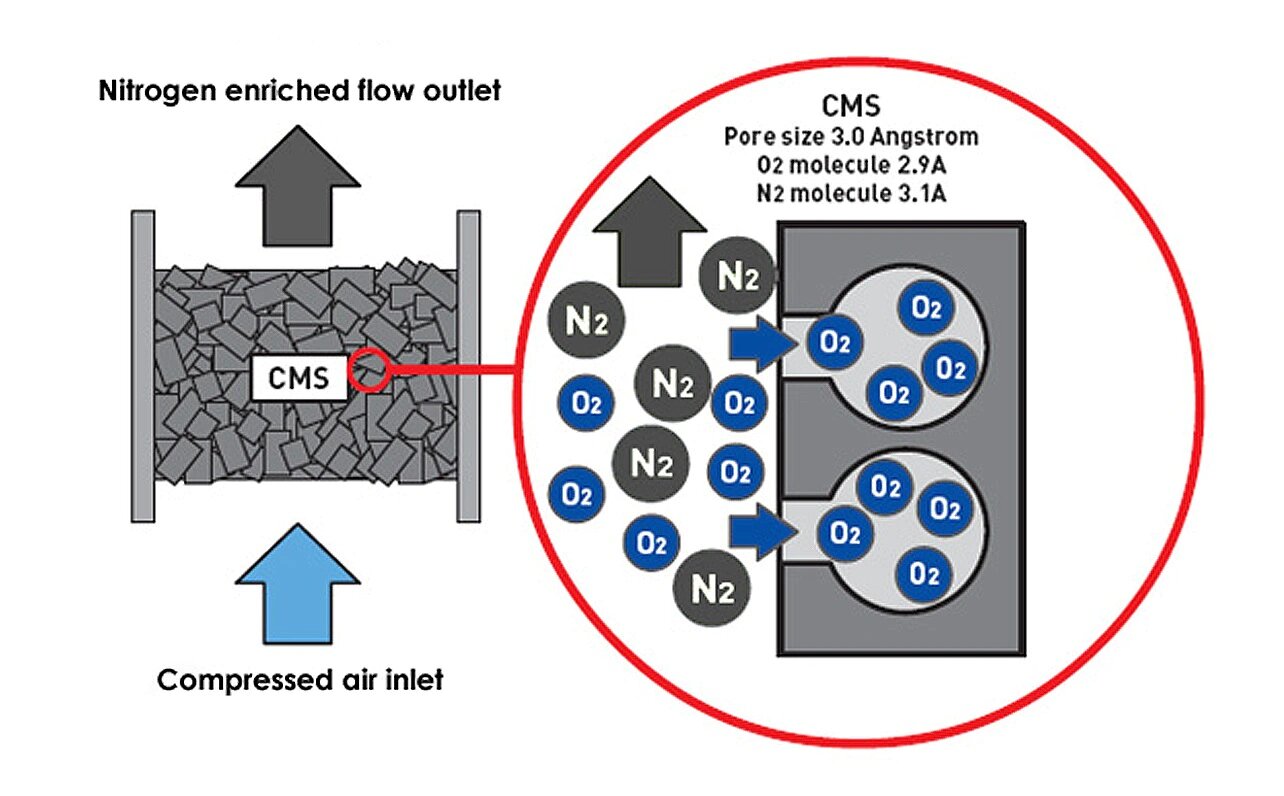
However, from the perspective of dynamics, because the carbon molecular sieve adsorbent is a-type rate separation adsorption agent, N2 and O2 are in the micropores of carbon molecular sieves in micropores There are obvious differences in the diffusion speed. For example, when: 35’C, the diffusion speed of O2 is 2.0×100, and the speed of O2 is 30 times faster than N2. Therefore ! (Separate in it, so that the N2 in the air can be purified.
Importance of Adsorption Time Control in the Separation Process
Because the adsorption separation process is a process of rate control, the control of the adsorption time (that is, the control of the adsorption-relief loop rate) is important. When the amount of adsorption agent, adsorption pressure, and gas flow rate are certain, the suitable adsorption time can be determined by determining the penetrating curve of the attached column.

Contact Xintao
If you have any question, please contact us!







