Jiangxi Xintao Technology Co., Ltd.
There is chemical industry there is Xintao chemical packing.
One function of molecular sieves is to adsorb various adsorbates on the outer surface of the crystal. Studies on molecular sieves have shown that their outer surface provides a precise molecular size that is adsorbed. If the molecules of the adsorbate exceed this size, they cannot enter the interior of the crystal and can only be adsorbed on the outer surface. Surface adsorption (also occurs on amorphous surfaces, such as silica gel), which is very weak, while there are thousands of crystalline voids and pores inside the crystal, which further adsorb molecules.
Molecular sieves are composed of silicon, aluminum and oxygen atoms. The ionic charges of these molecules should add up to zero in a stable crystal. To balance the positive and negative loads, positively charged ions such as potassium, sodium, and calcium are added. The huge surface with positive and negative ions is called the adsorption field. There is a strong attraction between the adsorbate and the adsorbate, and it takes a lot of energy (usually thermal energy) to eliminate the attraction and reduce it to a sieve. As the concentration of the adsorbate increases, the density charge field increases so that few layers of adsorbed molecules exist.
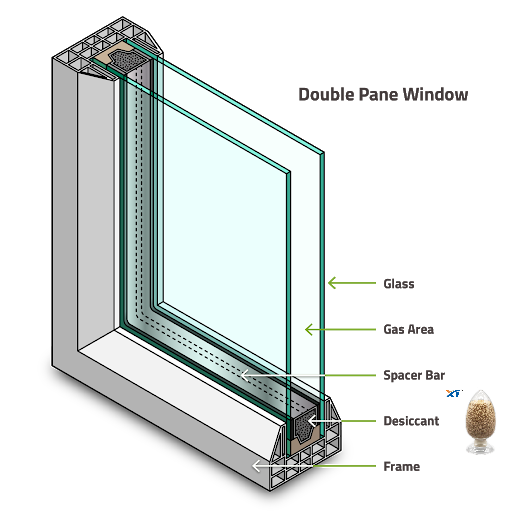
Eventually, the adsorbate is near full load and the pores are filled, similar to capillary condensation. If both water and benzene molecules enter the 13X crystal, both have the same chance of finding the charge field and adsorbing into the crystal, since both molecules are polar. However, some molecules like nitrogen and argon have no apparent polarity, so they may be weakly adsorbed to the crystal and easily replaced when a large influx of polar molecules occurs. During the adsorption process of molecular sieves, thermal energy is released to the surroundings. All of the molecular sieves we have now mentioned are capable of absorbing 20% of their weight in water at room temperature. Molecular sieve-filled insulating glass units can reach a low temperature dew point of -70°C with a few grams of desiccant.
The substances that can be absorbed by the desiccant in the insulating glass sealed unit include water, air, argon, krypton, xenon, sulfur hexafluoride and organic solvents. Fill the spacer layer with argon, krypton, xenon, sulfur hexafluoride gas to improve the U value and noise reduction performance of insulating glass. Organic solutions may come from sealing materials, cutting oils, and paint from the interior meg strips. Type 3A only absorbs water, type 4A absorbs water, air, argon, krypton, but does not absorb xenon, sulfur hexafluoride and solvents. Type 13X and silica gel absorb all of these substances.
Copyright © Jiangxi Xintao Technology Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved
We are here to help you! If you close the chatbox, you will automatically receive a responsefrom us via email. Please be sure to leave yourcontact details so that we can better assist